
| Google Scholar | Github | Email | Wechat | |
Hello there! I am Lixuan Guo, a third-year Undergraduate student majoring in Computer Science at Xidian University. Currently, I am a Research Intern
at Stony Brook University, advised by Chenyu You. I also collaborate closely with Yifei Wang and
Prof. Stefanie Jegelka to explore Sparsity's efficient and scalable applications in various fields, such as
embedding-based retrieval, LLM finetuning and MoE architecture design. Previously, I cooperate with Shixiong Zhang
on projects focusing on single-cell-RNA sequence clustering.
|
|
|
| abstract |
paper |
code |
project page |
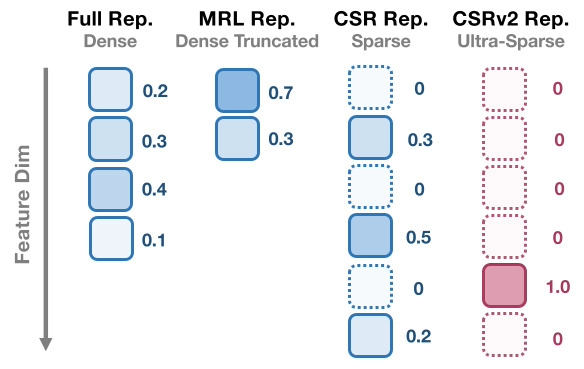
In the era of large foundation models, the quality of embeddings has become a central determinant of downstream task performance and overall system capability. Yet widely used dense embeddings are often extremely high-dimensional (e.g., 4096), incurring substantial costs in storage, memory, and inference latency. To address these, Contrastive Sparse Representation (CSR) is recently proposed as a promising direction, mapping dense embeddings into high-dimensional butk-sparse vectors, in contrast to compact dense embeddings such as Matryoshka Representation Learning (MRL). Despite its promise, CSR suffers severe degradation in the ultra-sparse regime (e.g., k ≤ 4), where over 80% of neurons remain inactive, leaving much of its efficiency potential unrealized. In this paper, we introduce CSRv2, a principled training approach designed to make ultrasparse embeddings viable. CSRv2 stabilizes sparsity learning through progressivek-annealing, enhances representational quality via supervised contrastive objectives, and ensures end-to-end adaptability with full backbone finetuning. CSRv2 reduces dead neurons from 80% to 20% and delivers a 14% accuracy gain at k = 2, bringing ultra-sparse embeddings on par with CSR at k = 8 and MRL at 32 dimensions, all with only two active features. While maintaining comparable performance, CSRv2 delivers a 7× speedup over MRL, and yields up to 300× improvements in compute and memory efficiency relative to dense embeddings in e5-mistral-7b-instruct-based text representation. Extensive experiments across text (MTEB, multiple state-of-the-art LLM embeddings (Qwen and e5-Mistral-7B), SPLADEv3, GraphRAG) and vision (ImageNet-1k) demonstrate that CSRv2 makes ultra-sparse embeddings practical without compromising performance, where CSRv2 achieves 7%/4% improvement over CSR when k = 4 and further increases this gap to 14%/6% when k = 2 in text/vision representation. By making extreme sparsity viable, CSRv2 broadens the design space for largescale, real-time, and edge-deployable AI systems where both embedding quality and efficiency are critical. |
|
|
| abstract |
paper |
Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures scale large language models (LLMs) by activating only a subset of experts per token, but the standard TopK routing assigns the same fixed number of experts to all tokens, ignoring their varying complexity. Prior adaptive routing methods introduce additional modules and hyperparameters, often requiring costly retraining from scratch. We propose Sequence-level TopK (SeqTopK), a minimal modification that shifts the expert budget from the token level to the sequence level. By selecting the top T \cdot K experts across all T tokens, SeqTopK enables end-to-end learned dynamic allocation -- assigning more experts to difficult tokens and fewer to easy ones -- while preserving the same overall budget. SeqTopK requires only a few lines of code, adds less than 1% overhead, and remains fully compatible with pretrained MoE models. Experiments across math, coding, law, and writing show consistent improvements over TopK and prior parameter-free adaptive methods, with gains that become substantially larger under higher sparsity (up to 16.9%). These results highlight SeqTopK as a simple, efficient, and scalable routing strategy, particularly well-suited for the extreme sparsity regimes of next-generation LLMs. |
|
| introduction |
code |
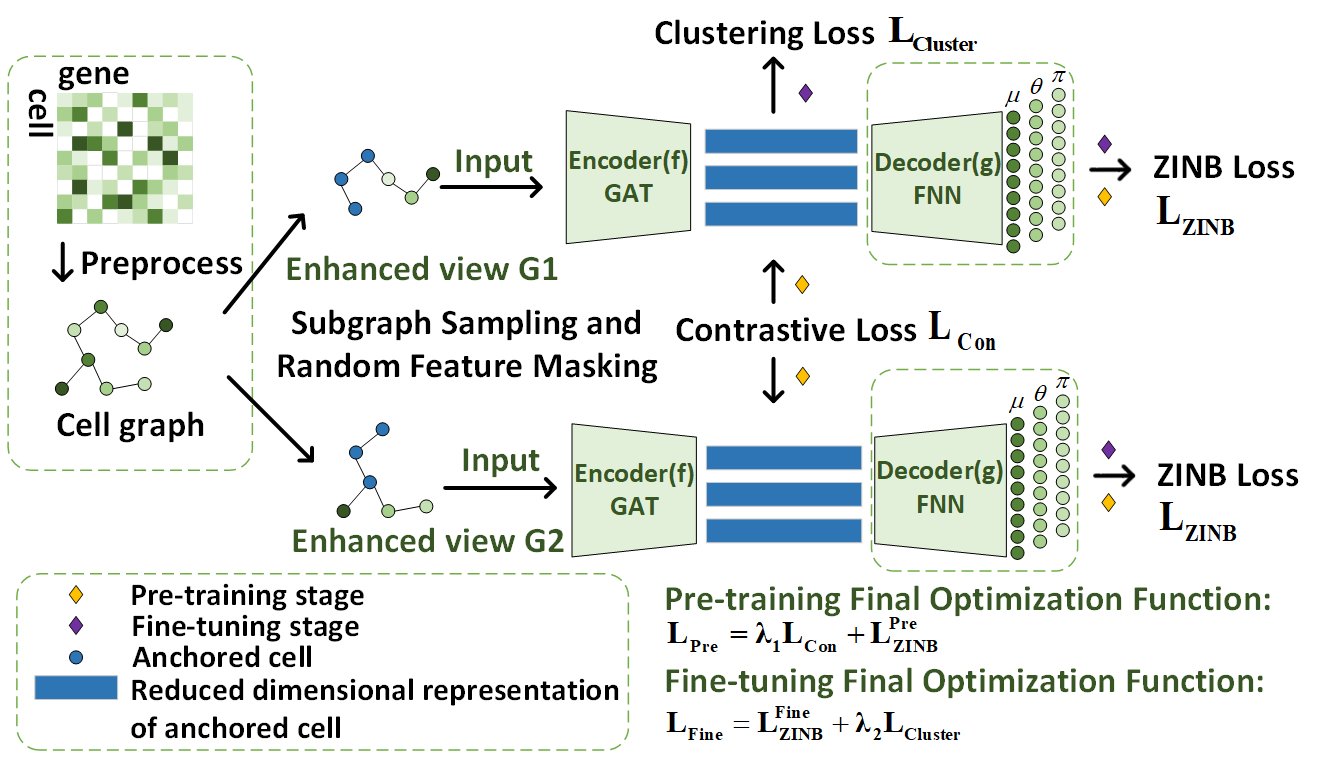
Cell clustering is crucial for analyzing single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data, allowing us to identify and differentiate various cell types and uncover their similarities and differences. Despite its importance, clustering scRNA-seq data poses significant challenges due to its high dimensionality, sparsity, dropout events caused by sequencing limitations, and complex noise patterns. To address these issues, we introduce a new clustering method called single-cell ZINB-based Graph Contrast Learning (scZGCL). This method employs an unsupervised deep embedding clustering algorithm. During the pre-training phase, our method utilizes an autoencoder based on the Zero-Inflated Negative Binomial Distribution (ZINB) model, learns cell relationship weights through a graph-attentive neural network, and introduces contrast learning to bring similar cells closer together. In the fine-tuning phase, scZGCL refines the clustering results by optimizing a loss function using Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence, enhancing the accuracy of cell classification into distinct clusters. Comprehensive experiments on 12 scRNA-seq datasets demonstrate that scZGCL outperforms state-of-the-art clustering methods. |
|
|
Template from this awesome website. |